Juniper publishers - The Performance and Association of Emergency Medical Technicians at Emergency Dispatch Encountering International Tourists
Abstract
Objective: To explore the self-satisfactory service and association of emergency medical technicians at facing emergency dispatch when encountering international tourists.
Method: Within the period from September to November in 2016, we delivered 970 questionnaires to Emergency Medical Technicians (EMT) who worked in the fire departments of Taipei City (220 copyies), Kaohsiung City (540), and Chiayi County (210). A total of 937 eligible respondents completed their responses with a return rate of 96.59%. Data including personal demography, technician expertise ability, emergency experience (34 items), foreign language ability, self-satisfactory service level, and suggestions to the issue for improving ambulance services treating international tourists (6 items) were collected. We (1) proposed a model with 7 hypotheses and used Smart-PLS software to examine their path coefficients effective, and applied Rasch model to calibrate item parameters of these two scales(i.e., 34items for experience in emergency and 6itemsfor suggestions).
Results: The results show that only 4 hypotheses were supported onto the proposed model. The three factors (i.e., foreign language ability, technician expertise ability, and emergency experience) can predict the self-satisfactory service level rather well. Only foreign language that can negatively influence suggestions to the issue for improving ambulance services treating international visitors. Item-person map using Rasch analysis shows that the most frequent incidence is the traffic accidence. The least occurrences are drowning, physical discomfort, heat failure, and heat cramps. The highest score endorsed by EMT on suggestions is to offer training courses associated with improvement of emergency ability in future. The rare suggestion with a low score is to set the APP in ambulance services used for treating international visitors.
Conclusion: The Partial Least Squares (PLS) path model using Smart-PLS can clearly explain the self-satisfactory service level that is predicted by three factors. Suggestions are recommended to relevant government departments for a reference applied to strategy planning and action taking in future.
Keywords: Foreigner; Tourist; Ambulance technician; Language; Travel
Abbreviations: EMT: Emergency Medical Technicians; MNSQ: Mean Square; PLS: Partial Least Squares; SEM: Structural Equation Modeling; TPB: Theory of Planned Behavior.
Introduction
With the increasing convenience of international tourism and traffic, people travelling to the world for sightseeing, overseas trips and the short-term jobs are also sharply increased. As Taiwan government launched a policy of the so- called "multi-dimensional layout to focus on the whole world” with a series of active marketing approaches, the foreign tourists have been seen with a rapid growth at an approximate 10.43 million tourists to Taiwan in 2015 [1]. A survey in 2015 conducted by a Taiwan magazine [2] reported that all citizens in a total of 10 cities and counties accounting for two-third Taiwan population being perceived with the prosperous phenomena of tourism improvement and development. Developing tourism becomes a major focus and directions for each mayor in Taiwan city governments.
The number of foreign tourists to Taiwan increased the number of emergency injuries and the call for helps dialing 911 is relatively increased. However, the foreign language faced by the Emergency Medical Technician (EMT) is a challenge due to the lack of standard operating practices and training course that can be applied to training EMT when facing foreign tourists at emergency treating situation. According to the statistics of foreign tourists treated by Taipei EMTs, the number has been increased 5.8 times from 115 tourists in 2006 to 667 in 2017. The top two sources in recent 10 years for Taipei city are attributed to common incidents (35%) and emergency diseases (26%). Others are those including general trauma, fall injury, car accident and roadside falls. The incidence of emergent illness is thus increased year by year with an obvious trend. The performance and association of emergency medical technicians at emergency dispatch facing international tourists are interesting topics worth exploring.
Emergency Medical Technician (EMT)
Emergency Medical Technician (EMT) and ambulance technician are terms used in some countries to denote a health care provider of emergency medical services. EMTs are clinicians, trained to respond quickly to emergency situations regarding medical issues, traumatic injuries and accident incidences. Under the Taiwan system, they are grouped into three types consisting of elemental EMT-1 (Emergency Medical Technician-1 needs 50-hour training course), Intermediate EMT-2 (Emergency Medical Technician-2 needs 280-hour training course), and paramedic EMT-P (Emergency Medical Technician-Paramedic needs 1280-hour training course), respectively.
Study hypothesis research model
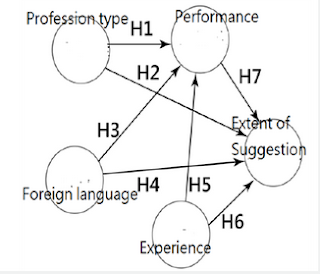
Ajzen [3,4] proposed Theory of Planned Behavior (TPB) in 1991, which is a rigorous theoretical framework to provide prediction and explanation of examinees' intentions to behavior. TPB has been successfully applied to provide a better interpretation of diverse behaviors in western settings [5,6]. According to TPB theory, three determinants--including attitude (i.e., whether I want to or not to support something), subjective norms (i.e., whether others encourage or limit me to support or not to support something), and perceived behavioral control (i.e., whether I have opportunities and resources to do or not to do something)--exert their effects on behavior through intentions [3] presented. Through the TPB, we can apply it to this study and define followings:
i. Suggestions from EMT (behaviors) can be affected by the EMT performance (intention),
ii. The one with a lower performance will raise more suggestion to the EMT team for further improvement, and
iii. EMT performance is affected by the types of EMT (i.e., attitude), personal experiences in EMT (i.e., subjective norms), and the foreign language ability (i.e., perceived behavioral control) (Figure 1).
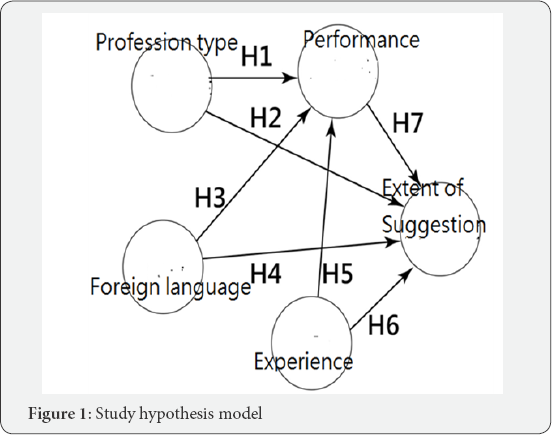
Using PLS-SEM for verity the research model effective
Partial least-squares(PLS) model [7-10], one of the Structural Equation Modeling (SEM) has been popularly used in many academic fields, such as management information [11], marketing [12], strategy management [13], accounting [14], family and business research [15], operation management [16], and in organizational research [17]. The method is currently regarded as suitable and, to some extent, a favorable alternative to the more restrictive traditionally used Covariance based SEM (CB-SEM) method [18]. In this study we are going to use PLS for exploring the performance and association of EMTs at emergency dispatch facing foreign tourists.
Aims of the study
This study aims at:
a. Verifying the seven hypotheses effective in Figure 1.
b. Analyzing the difficult scenes (i.e., occurrence frequency) EMT treated and experienced in Taiwan.
c. Disclosing the suggestions and rankings of their frequency raised by EMTs.
Methods
Data source and research tools
Within the period from September to November in 2016, we delivered 970 questionnaires to Emergency Medical Technicians (EMT) who worked in the fire departments of Taipei City (220 copies), Kaohsiung City (540), and Chiayi County (210). A total of 937 eligible respondents completed their responses with a return rate of 96.59%.
Questionnaire contents comprise personal demography, technician expertise ability, emergency experience (34 items), foreign language ability, self-satisfactory service level (one item), and suggestions to the issue for improving ambulance services treating international tourists (6 items). We verified the aforementioned study model with 7 hypotheses and used Smart-PLS software [19] to examine their path coefficients effective, and applied Rasch model [20] to calibrate item parameters of these two scales (i.e., 34 items for experience in emergency and 6itemsfor suggestions). The Likert-type 5-point ordered categories were applied to both 1-item self- satisfactory service and 6-itemsuggestion questionnaires. The higher score means the more performance and the stronger suggested tendency.
Data analysis
Four analyses were listed using description statistics as below:
a. Chi-square test was applied to verify the number of demographical characteristics (e.g., age, work tenure, education level) consistently distributed between variables and gentle.
b. The 34 dichotomous experience items (i.e., a binary response yes or no to the scene or incidence EMT faced in the past 2 years) were analyzed by Rasch model for calibrating parameters of item difficulty and person ability on a interval log it (=log odds) continuum using an item-person variable map (or say, Wright map in educational and psychometrical fields) [21,22].
c. The seven hypothesized path coefficients Figure 1 were verified by the bootstrapping method using Smart- PLS software [19]. The significant type I error is set at 0.05 level.
d. The suggestion item scores were analyzed by the Rasch Wright map to identify which one is harder (i.e., with a lower score) or easier (i.e., with a high score).
Using PLS-SEM for verity the research model effective
The reasons for the PLS-SEM path analysis [19] accepted by many academic researchers in recent years are those:
i. Not like CB-SEM requirement of large sample size and data following normal distribution random sampling;
ii. PLS-SEM is a non-parametric method with a lenient criterion of small sample size and data being distributionfree to investigate the cause-effect relation in a model [23,24];
iii. The PLS-SEM was developed in many published papers [5,6,25,26].
Rasch model
The Danish mathematician Georg Rasch formalized the requirements of invariance for measurement on data in a mathematical model which is unidimensional and probabilistic [19]. Since invariance is an integral property of the Rasch model, any test of the fit between the data and the model is a test of the extent to which the data show invariant properties with respect to the criterion of invariance tested if an instrument works invariantly across individuals or across sample groups depending on which test of invariance is assessed [27,28].
In this study we used Rasch model to analyze the difficulties(i.e., occurrence frequency) for items(i.e., scenes) EMT faced and experienced in the past two years, and disclose the suggestions to the issue for improving ambulance services treating international tourists and ranking their frequencies raised by EMTs.
Statistical tools and analyses
SPSS 22.0 for Windows (SPSS Inc., Chicago, IL) was used to conduct
i. The description statistics,
ii. Chi-square test on the consistent distribution of the number between demographical variables and the gentle.
Rasch Win steps software [29] was performed to estimate parameters. All the statistical significances were examined by the criterion of type I error at 0.05level.
Results
Demographical statistics
The sample includes male EMT accounting for 95.4%, female (4.6%) (Table 1). The age ranges are 30 or under (27.0%), 31~40(46.1%), 41~50(24.1%), and 51 or above (2.8%). In education level, the police college accounts for 57.5%, university (23.5%), and others (0.5%).
The job titles include team member (87.8%), chief (7.2%), captain (3.5%) and others (1.5%). The most number about service area is in Kaohsiung City (56.0%). The most work tenues are those 5 years or under (23.6%) and 6~10 years (23.2%). The types for EMT professional expertise are those EMT-2(86.0%), EMT-P (12.1%), and EMT-1 (1.9%). The self-assessment reports that 526 (56.8%) with competence in foreign language, and 411(43.2%) without confidence in dialogue or conversation using an appropriate foreign language. The count number of distribution is consistent and proportional to the pattern of gentle to other demographical characteristics such as job title, service area, and EMT profession type (Table 1).
The experience scenes and their frequencies
The Rasch item-person variable map(called Wright map) in Figure 2 shows that the In fit Mean Square Error (MNSQ) indices are all within 0.88 and 1.19(i.e., less than the criterion of 1.5), indicating the scale regarding the experience encountered in emergency scenes is unidimensional and probabilistic [19] fitting to the Rasch model rather well.
The most encountered incidence is traffic accidence. The least occurrences are those drowning, physical discomfort, heat failure, and heat cramps which are harder items (i.e., with a low frequency) shown at the top right-hand side. The easier (i.e., with a low number of count) items are shown at the bottom right-hand side in Figure 2. The average log it score across all items is zero. The person abilities are dispersed on the left-hand side. We can see that most persons are located below the reference at zero log it, indicating few EMT have the experience in emergency incidence encountered with foreign tourists. That is, the summation score is small in comparison with the total score (i.e., the 34 scenes or items).

Verifying the hypotheses in the study model
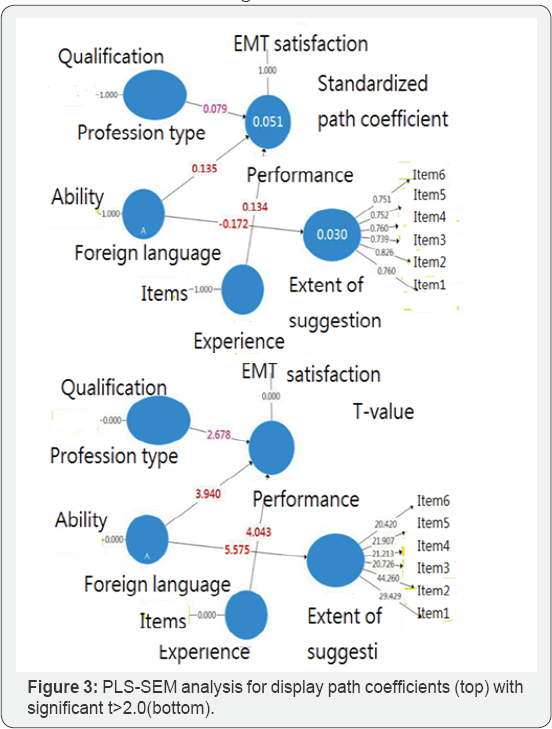
Using the bootstrapping method in PLS-SEM to examine the path coefficients effective for the study model (bottom in Figure 1), four hypotheses are supported when the t-value is greater than 2.0. There are foreign language ability, types of expertise, and the emergency experience, all of which significantly affect the self-assessment performance, see the bottom in Figure 3. In addition, the foreign language ability can negatively affect the extent of suggestion aspiration, indicating that those without confidence in foreign language yields a high score (or tendency) in suggestions to the issue for improving ambulance services treating international tourists.
The analysis of suggestion items using Rasch Wright map
The Rasch Wright map in Figure 4 shows that the Infit MNSQ are within 0.89 and 1.17 (i.e., less than the criterion of 1.5), indicating the scale of suggestions to the issue for improving ambulance services is unidimensional and probabilistic [19] fitting to the Rasch model pretty well.
The highest score endorsed by EMTs on suggestions is to offer training courses associated with improvement of emergency ability in future (see the bottom at the right-hand side in Figure 4). The rare suggestion with a low score is to set the APP in ambulance services used for treating international visitors (see the top at the right-hand side in Figure 4).
The person measures are dispersed at the left-hand side in Figure 4. Most of those respondents are located at the top greater than the item mean at zero logit, indicating that many endorsed this suggestion scale with a positive and concrete response to each item. A few with a low score at the left bottom around -2 logits in Figure 4 present extremely disagree responding to these listed suggestions.

Discussion
The results show that only 4 hypotheses were supported to the proposed model. Only three factors (i.e., foreign language ability, technician expertise ability, and emergency experience) can predict the self-satisfactory service level. The foreign language is the only one that can negatively influence suggestions to the issue for improving ambulance services treating international tourists.
Item-person map using Rasch analysis shows that the most frequent incidence is traffic accidence. The least occurrences are those drowning, physical discomfort, heat failure, and heat cramps. The highest score endorsed by EMT on suggestions is to offer training courses associated with improvement of emergency ability in future. The rare suggestion with a low score is to set the APP in ambulance services used for treating international visitors.
What This Adds to What Was Known
We verified that these three factors (i.e., foreign language ability, types of expertise, and the emergency experience) can affect the self-assessment performance. The result is consistent with the TPB model proposed by Ajzen [3,4] which reported that intention comes from three factors of attitude, subjective norms, and perceived behavioral control. The difference is that the intention (denoted by the personal self-assessment performance in this study) cannot predict the quantity of the suggestion in action (i.e., behavior). We can explain that the selfassessment satisfaction cannot be a reference to the suggestion tendency because some with high performance are reluctant, but some others are willing to express their own opinions for improving ambulance services. However, the foreign language ability is negatively associated with the quantity of suggestion, indicating the person with less confidence in foreign language raises more suggestions to the institute.
The Rasch Wright Map [20,21] has been popularly used in educational and psychometric fields [30]. The map is subject to the scores yielded by Rasch analysis [31] because only Rasch score that has been transformed to a logit score can be interval and additive.
The most and the least scenes encountered by EMTs are traffic accidence and those drowning, physical discomfort, heat failure, and heat cramps. The difference is beyond 6 logits. Basically on the interval basis, the odds is appropriately at 403(=exp(6)), which means that the probability to see a foreigner encountering traffic accidence is around 99.75% (=exp(6)/(1+exp(6))) frequently more than those rarely happened incidence above mentioned. The visualized representation using Rasch Wright map is easily interpreted and explained according to the item and person dispersion on an interval logit continuum.
What It Implies and What Should Be Changed?
The PLS-SEM in Figure 2 shows that these three factors (i.e., foreign language ability, types of expertise, and the emergency experience) can affect the self-assessment performance. Referring to policy of "multi-dimensional layout to focus on the whole world” launched by Taiwan government with a series of active marketing approaches, what main effort should be made is to strengthen the foreign language ability for EMTs as to increase their performance and service satisfaction in future.
Another main finding is the suggestions proposed most by those EMTs with less foreign language ability, see the negative coefficient (-0.172) in Figure 3. The urgent demand for the foreign language ability might be verified and supported in this survey.
Strengths of This Study
The framework of this study is to investigate the self- satisfactory service and association for EMT facing emergency dispatch when encountering international tourists that can be generalized to other relevant tourism businesses and industries, such as taxi, hotel, and police in foreign affairs.
Lee et al. [32] applied PLS-SEM to explore tourism behaviors and experiences from different cultural backgrounds to see tourists in Taiwan night markets, indicating that PLS-SEM is an appropriate method for use in investigating the tourism affairs.
By searching the PubMed database (Pubmed.com), we got 56 papers with the term of Emergency Medical Technician in title as of September 2, 2017, implying that EMT is a world-wide issue and attracts many researchers to study on the relevant topics. However, no such an EMT study like we did regarding the EMT foreign language ability was found in Medline library till now.
Limitations and Future study
The interpretation and generalization of the conclusions of this study should be carried out with caution. First, data were collected from Taiwan three government cities (i.e., Taipei, Kaohsiung, and Chiayi). The result from Figure 3 cannot be generalized to other cities or nations. Accordingly, it is worth mimicking the approaches used in this study to investigate more other EMT areas for further verifying the phenomena whether they are similar to the current study.
Second, we only put efforts on macro factors (e.g., foreign language ability, profession expertise, and EMT experience) instead of the micro features such as the confounder and mediator factors. Whether some demographical variables (e.g., gentle and age) that can intervene the prediction variable is merit to further investigate in future.
Third, the experience scale (34 items) was designed with a dichotomous format, not like the polytomous response perceiving the frequency of emergency incurrence so as to increase the test reliability. From Figure 2, we can see many EMTs on the left bottom part without any item (on the right bottom side) matched, which will decrease the test reliability due to the large measurement error in existence [31]. Finally, due to the research budget limitation, the current study merely collected data from Taiwan three government cities. Whether there is any difference found in other relevant businesses such as taxi, hotel, and police in foreign affairs is required for further studying.
Conclusion
The Partial Least Squares (PLS) path model using Smart- PLS can clearly explain the self-satisfactory service level that can be predicted by the three factors of foreign language ability, technician expertise ability, and emergency experiences. Suggestions to the issue for improving ambulance services treating international tourists are recommended to relevant government departments for a reference applied to strategy planning and action taking in future.
To Know More
About Trends in Technical
and Scientific Research Please click on:
https://juniperpublishers.com/ttsr/index.php
For more Open Access
Journals in Juniper Publishers please click on:
https://juniperpublishers.com/index.php
For more about Juniper Publishers Please click on:
https://www.zoominfo.com/c/juniper-publishers-inc/370428819



Comments
Post a Comment