Production of Antibiotic Free Chicken and in-vivo & In-Vitro Evaluation of Atomes Novel Antibiotic Replacement Biotechnology, Novo Biotic ®, in Broiler Chicken Compared to Antibiotic Growth Promotors Avilamycin - Juniper Publishers
Trends in Technical & Scientific
Research
Abstract
A Patented Novel Antibiotic Replacement Technology (ART) Novo Biotic ® (Multi-Strain spores forming Bacillus FD 777) was validated in-vivo & In-Vitro based on its potentialities and capabilities of producing 15 complex of enzymes and more than 34 types of Lipopeptides (Bio-Antibiotics) in the production of broiler chicken. A total of 53’120 one-day-old ROSS 308-AP chicks were placed in 6 blocks and reared to 40 days. Control groups treated with Antibiotic Growth Promotor Avilamycin at 150g per Ton of feed, groups treated with Avilamycin at 150mg per ton of feed and Novo Biotic ® at 1L per 1000L of drinking water for 7 days and later 4 days per week till Day of Depletion (DOD between 38 and 40 days), and a group only treated with Novo Biotic ® at 1 L per 1000L of drinking water for 7 days and later 4 days per week till the DOD. The mean of the cumulative results of 1 to 40 days age revealed that birds treated with Novo Biotic ® with Avilamycin showed an FCR of 1.56 meanwhile the groups control treated only with AGP showed and FCR of 1.67. The treated group only with Novo Biotic ® showed an FCR at 1.53 compared to 1.67 of the control group. It’s clear that the AGP is affecting the performance of the Bacillus Strains in the Novo Biotic ®. With the best FCR 1.53 obtained with only Novo Biotic ® vs AGP alone 1.67, along with the In-Vitro studies against Salmonella, E. Coli, Pseudomonas aeruginosa, Staphylococcus aureus with an inhibition zones between 25mm to 30mm, the Novel Novo Biotic ® is considered as an “ART” unique in its category, by preventing challenges and promoting an optimum Broiler performance.
Keywords: Novo biotic ®; FCR; EPEF; Antibiotic growth promoters (AGP); Probiotic; Elisa
Introduction
Antibiotic growth promoters (AGPs) have been widely used to improve the performance of Broilers and the food conversion rates and they are well documented [1]. Antimicrobials are given to broiler chicken to control diseases such as necrotic enteritis caused by Clostridium species [2-6] in addition to Salmonella Species [7-9] and E. Coli, [10,11]. Antibiotics have started to fail. The rapid emergence of resistant bacteria is occurring worldwide, endangering the efficacy of antibiotics, which have transformed medicine and saved millions of lives [12,13]. Resistant bacteria already causing more than 750,000 deaths every year and scientists did not introduce any new molecule since 1987. 106 million new cases/year are being seen and the consequences of total resistance would be devastating. This number is predicted to rise dramatically if radical actions are not taken. More than 60% of the populations in some areas carry multidrug-resistant bacteria in their normal bacterial flora. 214,000 newborns are estimated to die every year from blood infections (sepsis) caused by resistant bacteria - representing at least 30% of all sepsis deaths in newborns [14-22].
Antimicrobial resistance (AMR) is a global health threat and antimicrobial usage and AMR in animal production is one of its contributing sources [22,23]. Poultry is one of the most widespread types of meat consumed worldwide and are often raised under intensive conditions using large amounts of antimicrobials to prevent and to treat diseases, as well as for growth promotion [24]. Researchers estimate that the global average annual consumption of antibiotics per kilogram of chicken produced is 148 mg/kg [25]. Chicken harbors large proportion of Enterobacteriaceae resistant to aminosides in its digestive tract and tetracycline in its meat [26]. Another Canadian study [27] highlights the existence of different stereotypes of Salmonella, isolated from broiler farms, resistant and multi-resistant to antibiotics. In addition, antibiotic resistance in Enterococci [19], Mycoplasma Gallisepticum [28] and Salmonella spp. [29] isolated in broilers have been reported.
AGPs have been banned in more than 30 countries worldwide, mainly due to concerns about human health and the emergence of superbugs, or bacteria resistant to multiple types of antibiotics. Thirty-five countries have a veterinary prescription requirement [3,4,19]. The European Commission (EC) decided to ultimately ban (January 1, 2006) all commonly feed antibiotics used as growth promoters (EC Regulation No. 1831/20031) [30,31]. Finding alternatives of AGP is now a viable solution to save the livestock sector. Probiotics have been proved to be the most preferred and effective alternative to antibiotics as a growth promoter and pathogens inhibitor in poultry industry [32-34]. In this study both In-Vitro and in-vivo evaluation of a Patented Biotechnology based product originated 100% from biofermenation, Novo Biotic ®, produced by Atomes FD. Inc. Canada was evaluated against an antibiotic growth promoter (AGP) Avilamycin.
Novo Biotic ® is an innovation patented product that is used as 2 in 1 product:
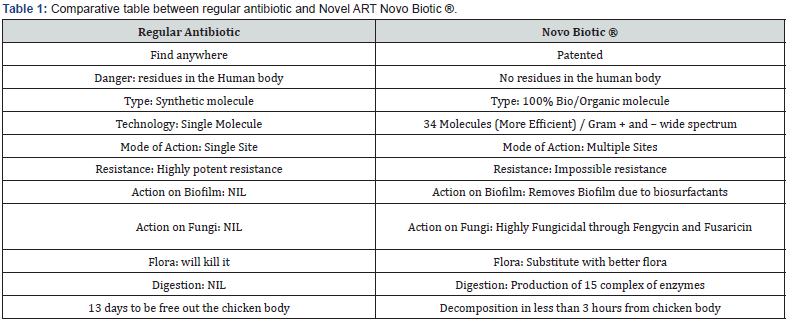
1- Probiotic with a minimum of 1 billion CFU per ml of patented Bacillus FD777 multi-strains spore forming for its capability of producing more than 15 complexes of enzymes. Antibiotic Replacement Technology (ART) for its capability of producing more than 34+ types of bio antibiotics (Lipopeptides). All previous studies showed a complex of 34 Lipopeptides expressed genetically on the FD 777 strains such as: Macrolactin, Bacillomycin, Bacillaene, Fusaricidin, Difficidin, Bacitracin, Iturin, Tridecaptin, Bacilysin, Plipastatin, Surfactin, Teichuronic acid, Bacteriocin, Subtilin, Bacillibactin, Locillomycin, Kalimantacin, Myxovirescin, Plantathiazolicin, Citrulline, Plantazolicin, Bacitracin, Batumin, Nosperin and Fengycin (Table 1).
Materials & Methods
In-Vitro Analysis
Novo Biotic ® Multi-strains FD 777 has the capability of producing 34 types of Lipopeptides which has a wide spectrum of killing effect on Salmonella, E. Coli, Pseudomonas aeruginosa, Clostridium, Staphylococcus aureus etc.
Below procedure describes the In-Vitro killing test of Novo Biotic ® against:
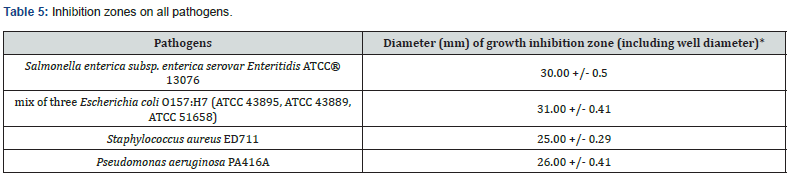
a) Salmonella enterica subsp. enterica serovar Enteritidis ATCC® 13076
b) mix of three Escherichia coli O157:H7 (ATCC 43895, ATCC 43889, ATCC 51658)
c) Staphylococcus aureus ED711
d) Pseudomonas aeruginosa PA416A
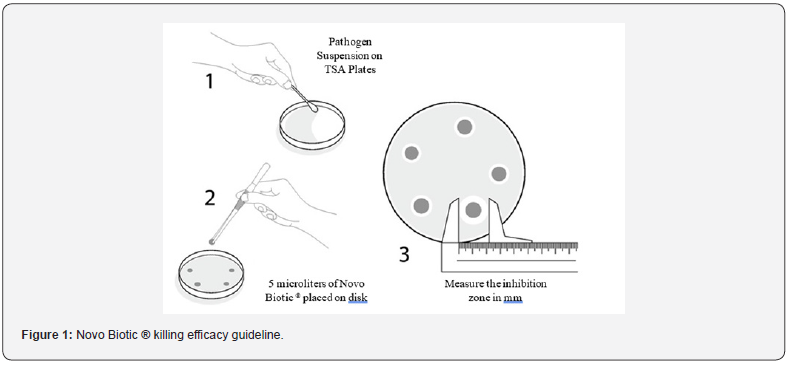
i. 50 microliters of the above bacterial (Pathogen) were incubated overnight at 37oC in 20ml of Tryptic Soy Broth at 200rpm shaker.
ii. 100 microliters of the suspension were spread onto TSA plates, Trypticase Soy Broth with 1.5% Agar except for the staphylococcus which contains 0.25% Agar.
iii. 5 microliters of Novo Biotic ® (1/1000 dilution) were deposited on a disk on lawns of the above pathogens.
iv. Plates were incubated at 25oC for 48 hours.
v. The inhibition zones (Clear haloes) were measured in mm as below Figure 1. guideline.
In-Vivo Analysis
Birds Husbandry
One-Day-Old Ross 308 AP as hatched broiler chicks were delivered to the farm located in south of Lebanon during December 2019. All farms are semi-open system. The environmental conditions including temperature, humidity and ventilation of the farm were maintained and regulated according to the Aviagen breeder guidelines, by an automatic climate controller during the trial.
Feed Dietary and Treatment
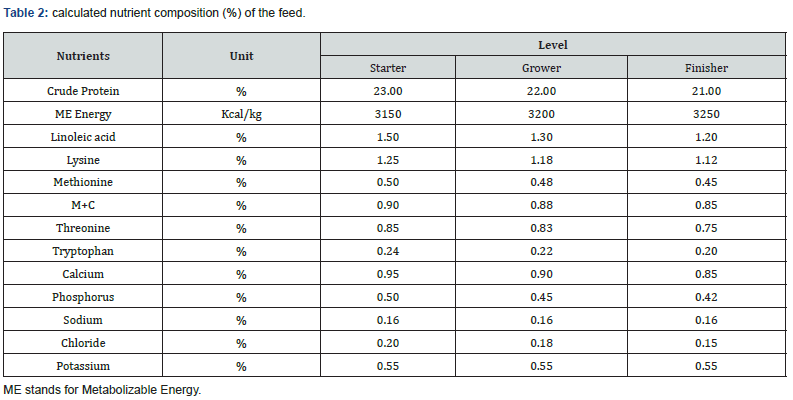
A 3 phases feeding program was followed: starter (fed from day 0 to 14), grower (fed from 14 to 28), finisher (fed from 28 to 35).
The nutrient value of the feed given by the supplier is shown in Table 2.
Experimental Design
Trial was conducted as per below design:
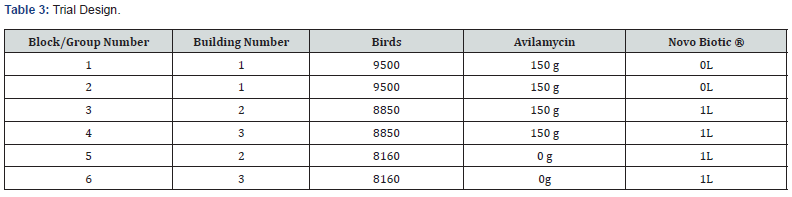
a) Block 1: 9500 Birds considered as control whereas Avilamycin is added 150g per DMton of feed. No Novo Biotic ® is added to drinking water.
b) Block 2: Replica of Block 1 with 9500 Birds. whereas Avilamycin is added 150g per DMton of feed. No Novo Biotic ® is added to drinking water.
c) Block 3: 8900 Birds whereas feed still containing Avilamycin 150g per DMton and added Novo Biotic ® to the drinking water at 1L per 1000L first 7 days and later 1L per 1000L of drinking water 4 days a week till DOD.
d) Block 4: Replica of Block 3 with 8160 Birds whereas feed still containing Avilamycin 150g per DMton and added Novo Biotic ® to the drinking water at 1 L per 1000 L first 7 days and later added 1 L per 1000 L of drinking water 4 days a week till DOD.
e) Block 5: 8900 Birds whereas Avilamycin stopped from the feed and only added Novo Biotic ® to the drinking water at 1L per 1000L first 7 days and later added 1L per 1000L of drinking water 4 days a week till DOD.
f) Block 6: Replica of Block 5 with 8160 Birds whereas Avilamycin stopped from the feed and only added Novo Biotic ® to the drinking water at 1L per 1000L first 7 days and later added 1L per 1000L of drinking water 4 days a week till DOD.
Table 3 clearly summarize the combination:
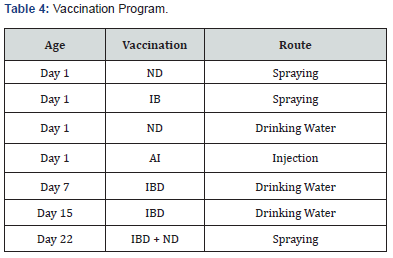
Vaccination Program
Vaccination was performed as per below table (Table 4).
Broiler Performance
Body Weight (BW) and Feed Intake (FI) were recorded weekly (day 0, 7, 14, 21, 28, 35 and at DOD) as an average per Block. The feed conversion ratio (FCR) is the amount of feed ingested by an animal which can be converted into one kilo of live weight. The economic FCR is calculated as per below formula:
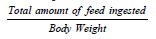
Body Weight is the weight of animals that can be accepted at the slaughterhouse. Feed conversion ratio (FCR) adjusted for mortalities was calculated for each Block. Mortality rate per treatment was calculated for the entire trial period. All results are calculated based on the average between block 1 and 2, block 3 & 4 and block 5 & 6. European Production Efficiency Factor also was calculated as per below formula:
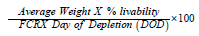
Serological Analysis
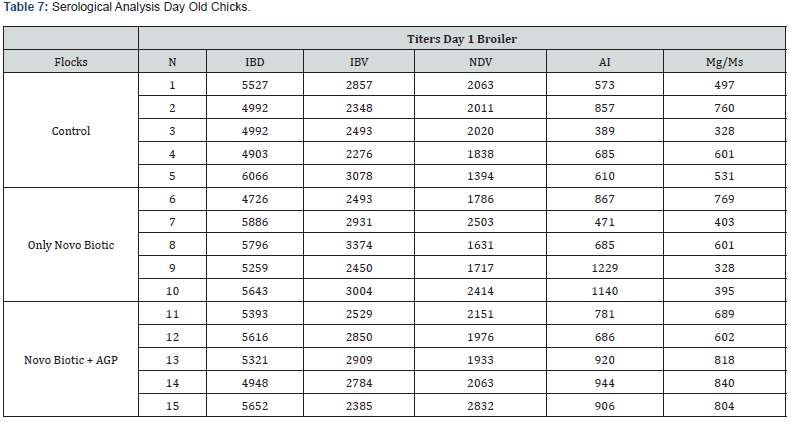
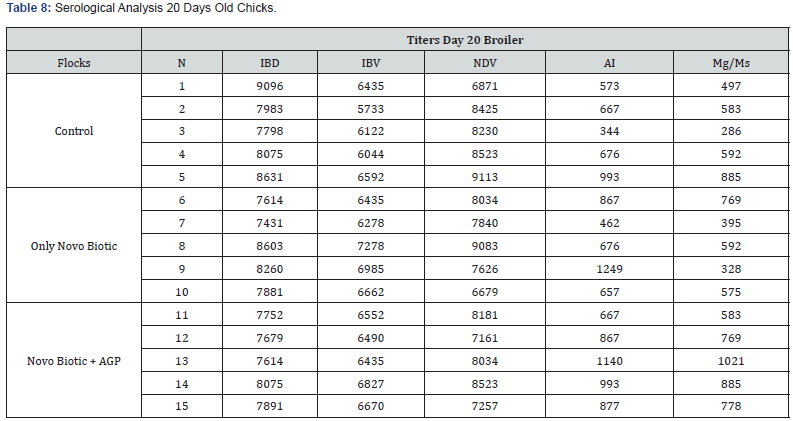
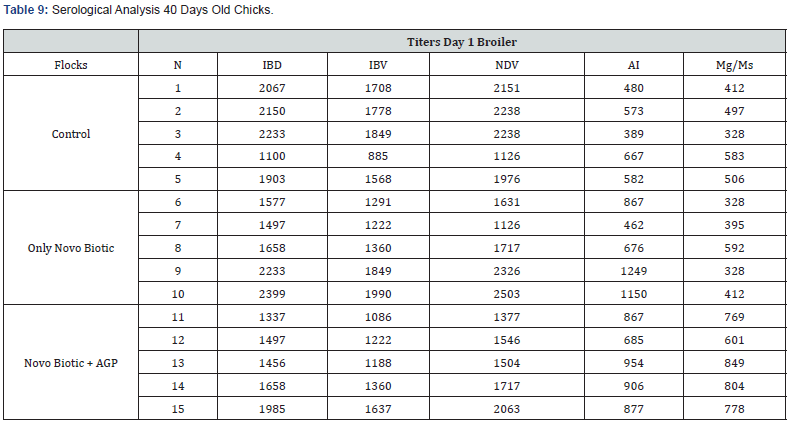
5 Blood samples were taken from each group of blocks. With three groups total will be 15 samples per reading. Samples were tested (titers) for IBD (Infectious bursal disease), IBV (avian infectious bronchitis virus), NDV (Newcastle disease virus), AI (Avian Influenza) and MG/MS (Mycoplasma). Titers noted for days 0, Days 20 and Days 40.
Statistical Analysis
Statistical analysis was performed using online statistical tools. The significance between treatments was determined by an analysis of variance with the general linear model. In all cases the level of statistical significance was P < 0.05 (Table 5).
Screening for Extracellular Enzymatic Activity of Novo Biotic ®
In order to quantify the International Units of the enzyme, thermofisher test kits were used.
Results & Discussion
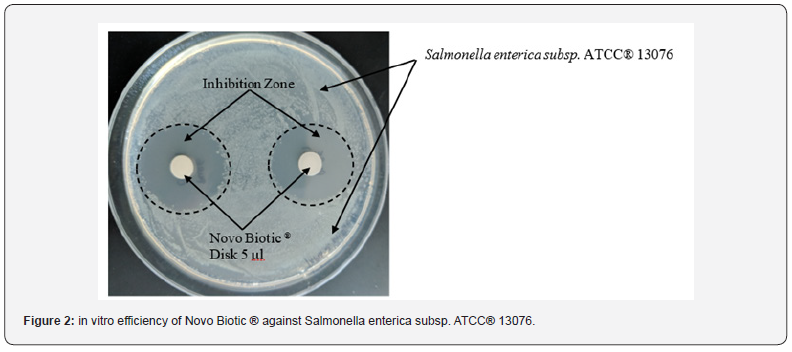
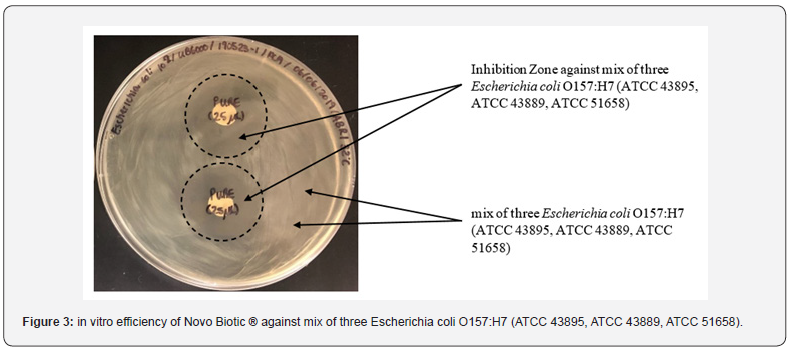
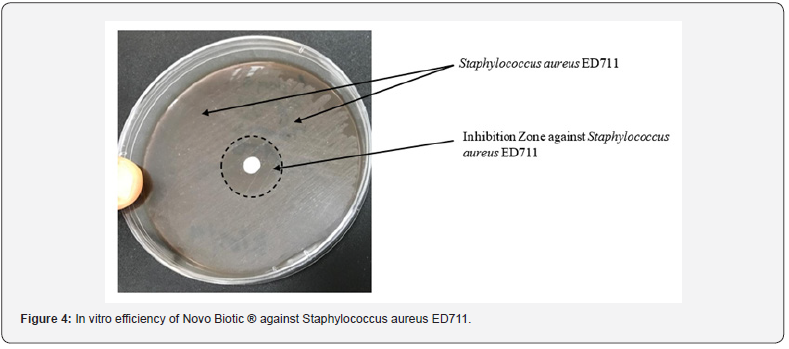
In-Vitro Analysis Below figures describe the test results along with the inhibition zones. (Figures 2-4)
Broiler Performance
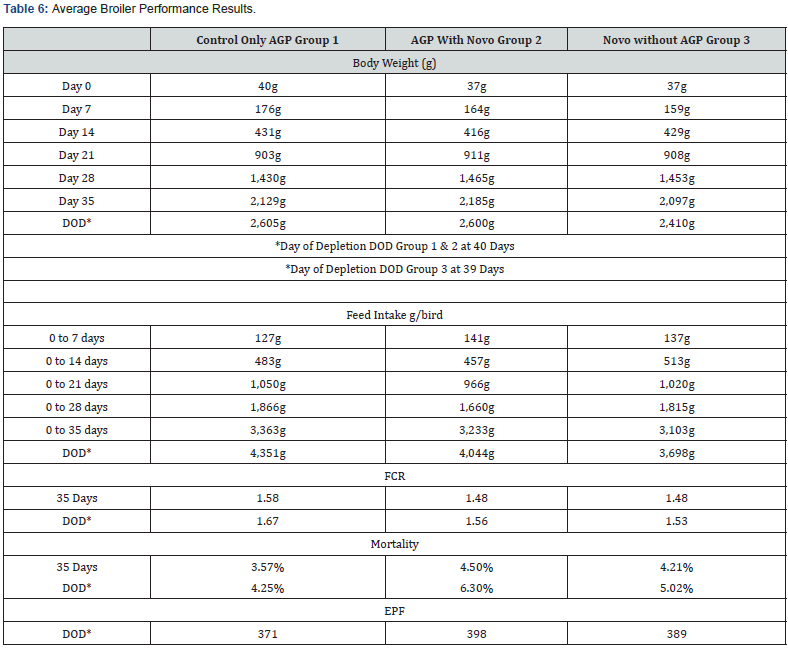
Table 6 shows all results calculated based on the average between block Group 1 (mean of Blocks 1 and 2), Group 2 (mean of Blocks 3 & 4) and Group 3 (mean of Blocks 5 & 6).
Serological Analysis
Tables 7-9 reveal all serological analysis at day old chicks, 20 days and 40 days, prior depletion.
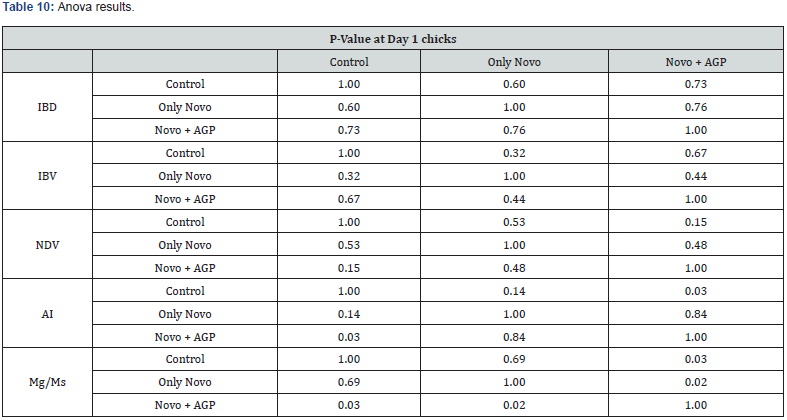
Anova Results as below table
Table 10 summarizes the Anova analysis of the serological results performed on day 1 old chicks between group for every disease. Majority of the analysis showed no significant difference at P < 0.05 except for the:
a) Avian Influenza between the control group treated only with AGP and the group treated with AGP and Novo Biotic at 0.03 < 0.05
b) Mg/Ms titers between: firstly, the Groups the control treated with AGP and the one treated with AGP and Novo Biotic and secondly between the group treated with only Novo Biotic and the group treated with Novo Biotic and AGP at 0.02 < 0.05
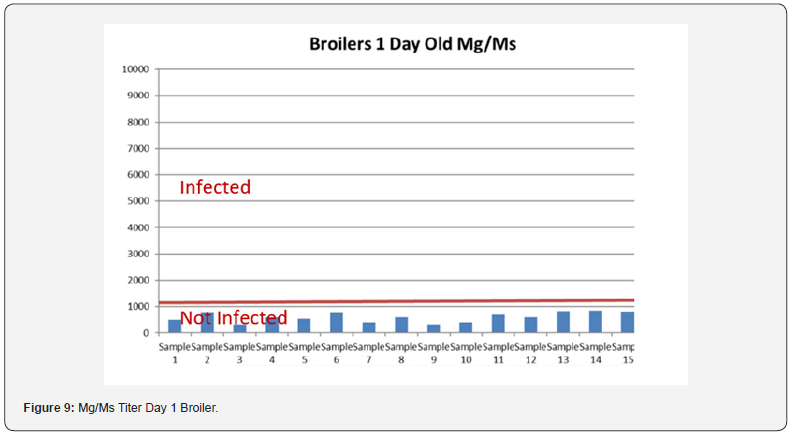
In order to better interpret the results below charts reveals the titers of the 3 groups for every disease along with the disease evaluation (Figures 5-9). All flocks were being protected and uninfected for all the diseases as all titers are below the infection baseline.
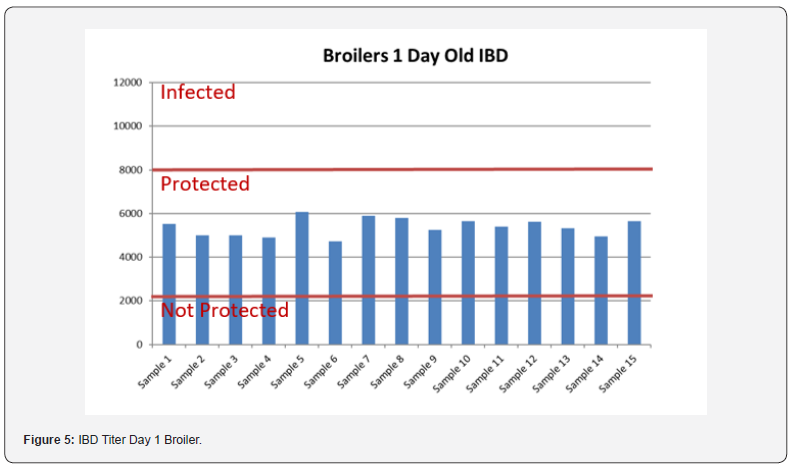
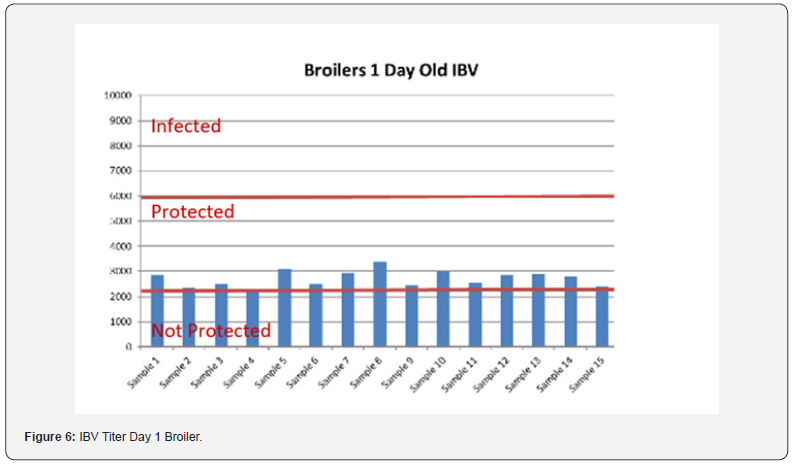
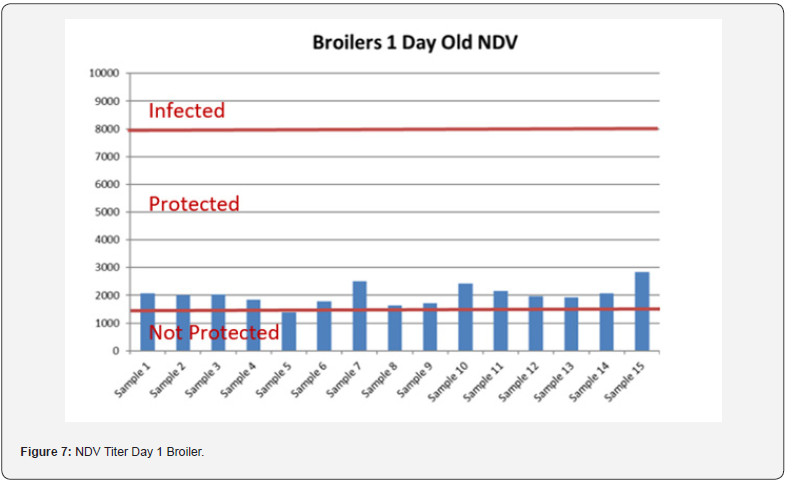
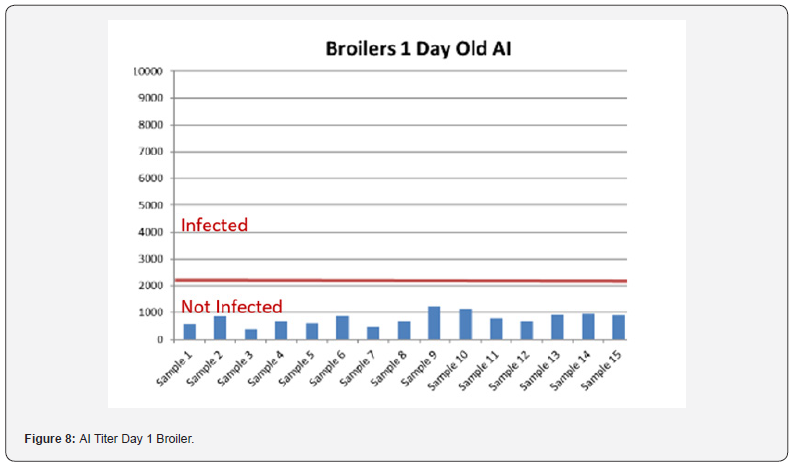
Anova Results as below table
Table 11 summarizes the Anova analysis of the serological results performed on day 20 old chicks between group for every disease.
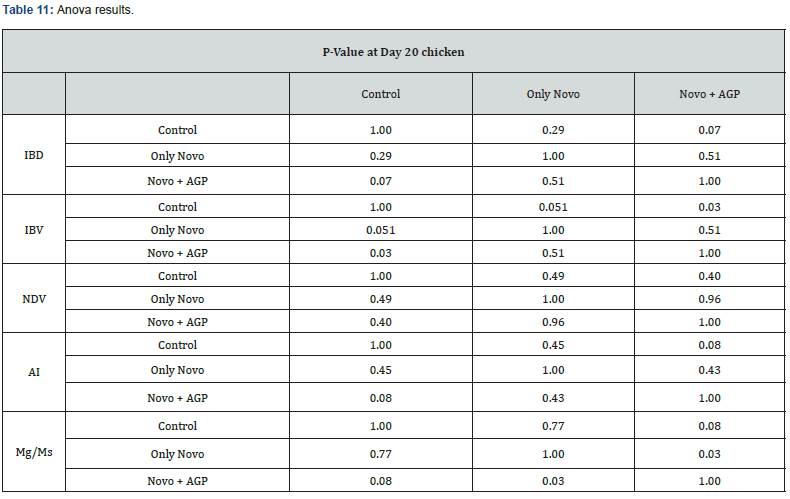
Majority of the analysis showed no significant difference at P < 0.05 except for the:
c) IBV between the control group treated only with AGP and the group treated with AGP and Novo Biotic at 0.03 < 0.05 d) Mg/Ms titers between the group treated with Novo Biotic alone and the group treated with Novo Biotic and AGP at 0.03 < 0.05
In order to better interpret the results below charts reveals the titers of the 3 groups for every disease along with the disease evaluation (Figures 10-14). All flocks were being protected and uninfected for all the diseases as all titers are below the infection baseline.
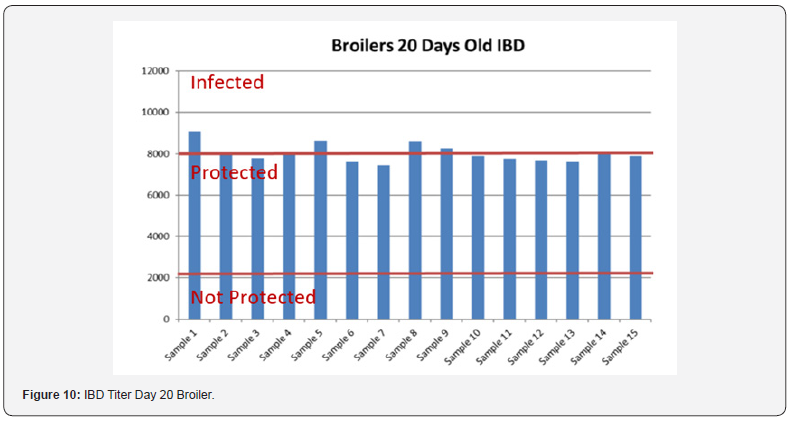
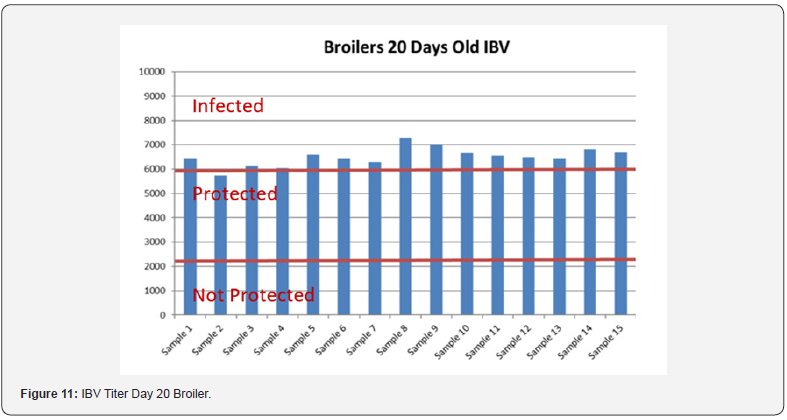
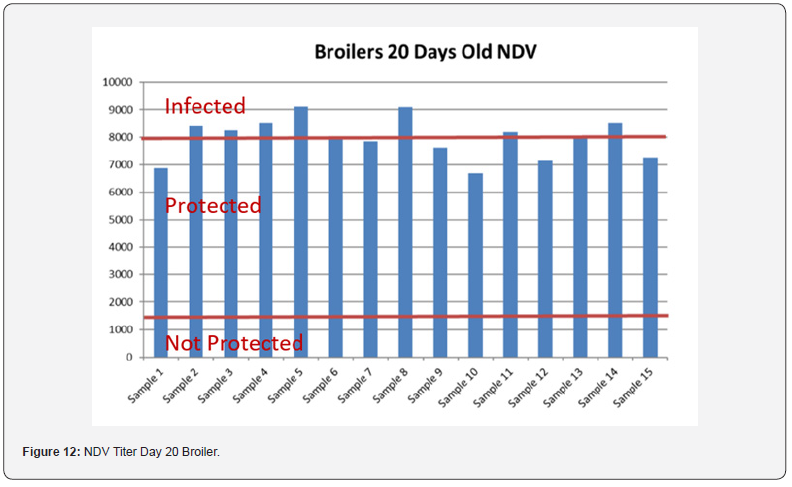
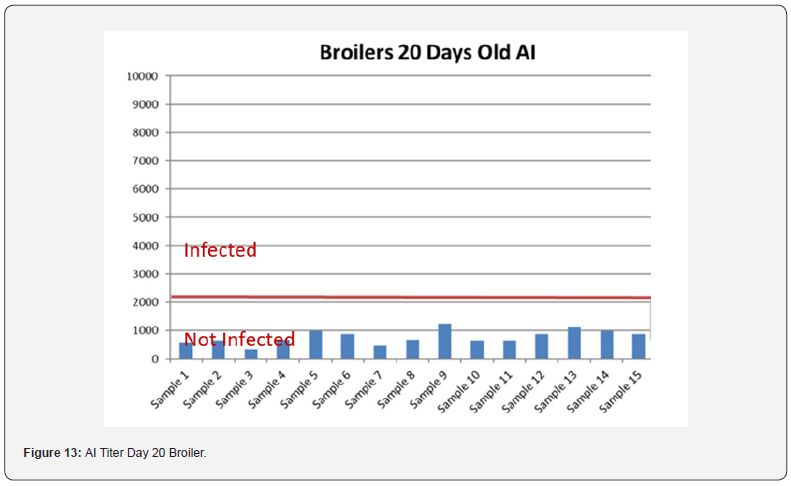
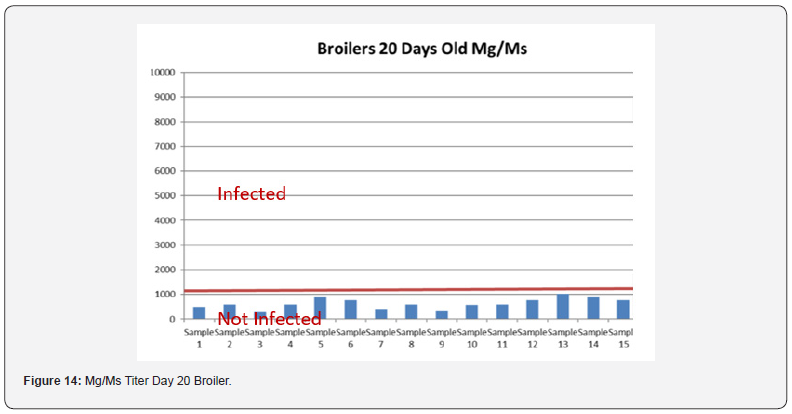
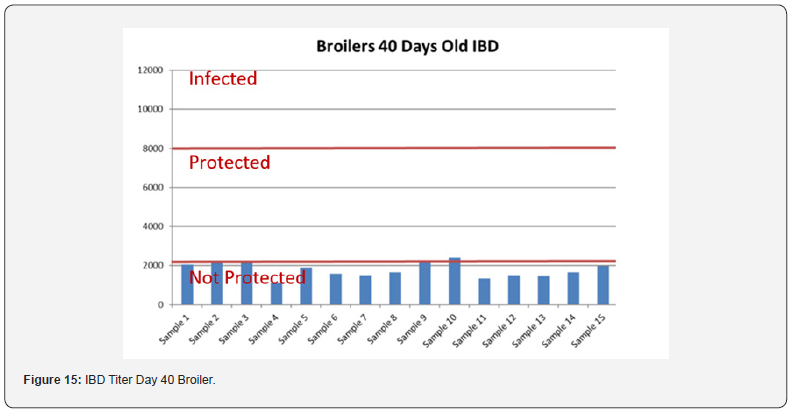
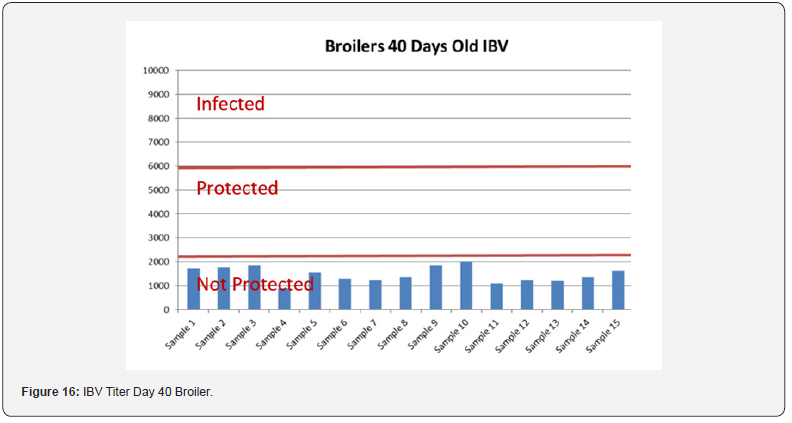
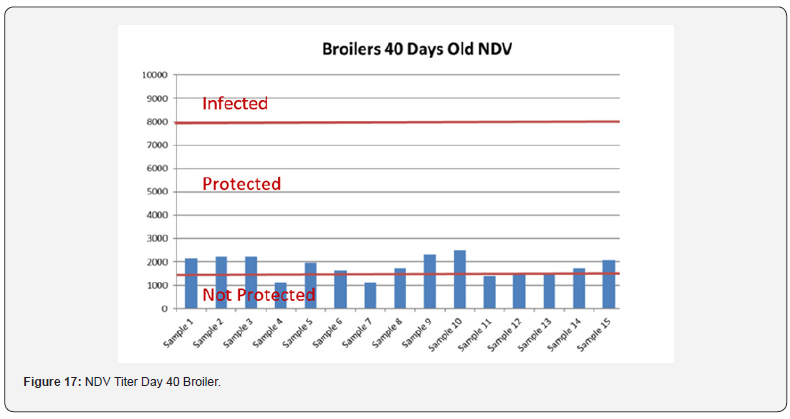
Table 12 summarizes the Anova analysis of the serological results performed on day 40 old chicks between group for every disease. Majority of the analysis showed no significant difference at P < 0.05 except for the:
e) NDV between the control group treated with AGP and Novo Biotic at 0.02 < 0.05
f) AI titers between the group control and the group treated with Novo Biotic + AGP at 0.00 < 0.05
g) Mg/Ms titers between the control group treated only with AGP and the group treated with AGP and Novo Biotic at 0.00 < 0.05 & between the group treated with Novo Biotic alone and the group treated with Novo Biotic + AGP at 0.00 < 0.05
In order to better interpret the results below charts reveals the titers of the 3 groups for every disease along with the disease evaluation (Figures 15-19). All flocks were being protected and uninfected for all the diseases as all titers are below the infection baseline. Although Anova results revealed some significant differences but all above serological titers show protection in some cases but uninfected flocks in all cases (Table 13).
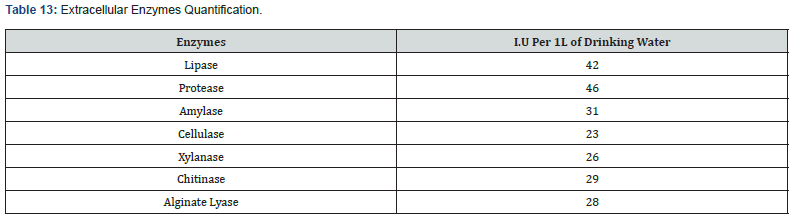
Screening for Extracellular Enzymatic Activity of Novo Biotic ®
The bacterial strains of the Bacillus FD777 isolates, after 10 minutes of adding in the drinking water, presented extracellular enzymatic activity as below:
Conclusion
a) When adding Novo Biotic ® to AGP and comparing group 1 and 2 we can clearly see that FCR of group 2 (1.56) is way better than FCR of Group 1 (1.67). Novo Biotic ® promoted the development of positive bacterial flora in the digestive system of the chicken. The FD 777 Strains populations in the GIT are associated with enhanced animal performance, reflecting more efficient digestion and improved immunity. The FD 777 increased the digestion and absorption of nutrients essentially the amino acids due to high production of Protease also specially the amylase which also increase the body weight gain and improvement in feed use efficiency. Previous studies and analysis on Novo Biotic ® Studies show a complex of synergy between the activity of 15 complexes enzymes to include: Protease, metalloproteases, Amylase, Lipase, Esterase, urease, Xylanase, Cellulase and Phytase.
b) By removing the Avilamycin AGP and keeping Novo Biotic ®, we can clearly notice a better drop in the FCR between Group 2 (1.56) and Group 3 (1.52) and this is due the effect of the AGP on the Novo Biotic ® performance. Accordingly, always stop AGP from feed while using Novo Biotic ® to have the optimum performance of the FD 777 strains. Dropping the FCR from 1.67 to 1.53 and stopping the AGP has a substantial ROI (Return on Investment) to the client.
c) At 1 L per 1000 L of water as per above program, Novo Biotic ® completely replaces the Avilamycin AGP with better FCR (approx 14 points) accordingly the farmer can claim Antibiotic free chicken.
d) Due to 34 + Lipopeptides, Novo Biotic ® has the ability to complete inhibit and kill the pathogens such as E. Coli, Salmonella, Pseudomonas and Staphylococcus with a minimum inhibition zone of 25 mm.
To Know More About Trends in Technical and Scientific Research Please click on:
https://juniperpublishers.com/ttsr/index.php
To Know More About Open Access Journals Please click on:
https://juniperpublishers.com/index.php




Comments
Post a Comment