Juniper Publishers - Digital Literacy and its Use by Teacher Trainees at Secondary Level in Odisha
Trends in Technical & Scientific Research
Abstract
Digital devices and applications have been used in schools and teacher education institutes across the globe for teaching learning. All the prospective teachers must be digitally savvy to utilize it in school for teaching, assessment, management and professional development. This study intended to find out the level of digital literacy and its uses among teacher trainees at secondary level. Descriptive research method was followed for undertaking this study. Survey was conducted on sample of 170 trainees selected randomly from teacher education institutes under Utkal University, Odisha, India. Self-developed questionnaire based on different aspects of digital devices and applications such as skills of trainees in digital technology, use of digital technology and applications by trainees for learning and teaching etc. was used at tool. Collected data were subjected to frequency and percentage analysis and accordingly conclusions were drawn. The study found that majority of trainees can change screen brightness and contrast, minimize, maximize and move window screen, use search command to locate a file and download and install applications, more than 50% of trainees do not know learning management system, virtual worlds, podcasts and web design applications, around 70% of trainees are aware about storage of video in camera, manage junk mail and update username and password and less than 50% of trainees knew about voice typing and cyber security, majority of trainees use group email and WhatsApp for academic work and only 20% of trainees use digital devices for using PPT in class, create digital learning materials, provide feedback to students. It is suggested that teacher education institutes must be equipped with digital devices and applications useful for teaching learning and professional development. Further, teacher educator must encourage and motivate trainees by integrated ICT in regular course work and across the subjects so that trainees can develop skills of using it for teaching, learning and assessment in schools.
Keywords:Digital Literacy; Digital Devices; Applications; Teacher Trainees; ICT
Conceptualization of the Problem
Digital literacy is the engine of the modern civilization and the driving force of the information age. Today the meaning of literacy is not just limited to the ability to read and write. It extends to an effective application of all those activities in which literacy is normally assumed. The modern meaning has been expanded to include the ability to use language, numbers, images, computers, and other basic means to understand, communicate, gain useful knowledge, solve mathematical problems and use the dominant symbol systems of a culture. In this context, digital literacy has become much more than the ability to handle computers, just like traditional literacy and numeracy, it comprises a set of basic skills which include the use and production of digital media, information processing and retrieval, participation in social networks for creation and sharing of knowledge, and a wide range of professional computing skills. The UNESCO [1] Expert Meeting in Paris, defined “literacy is the ability to identify, understand, interpret, create, communicate, compute and use printed and written materials associated with varying contexts. Literacy involves a continuum of learning in enabling individuals to achieve their goals, to develop their knowledge and potential, and to participate fully in their community and wider society”.
Different committees and commissions in India have strongly recommended for the use of ICT and digital technology in the education system for increasing its efficiency. The National Policy on Education (1986) stressed the need to employ educational technology to improve the quality of education. The significant role that ICT can play in school education has also been highlighted in the National Curriculum Framework [2]. Use of ICT for quality improvement also figures in Government of India’s flagship program on education, Sarva Shiksha Abhiyan (SSA). Again, ICT has figured comprehensively in the norms of schooling recommended by the Central Advisory Board of Education (CABE), in its report on Universal Secondary Education, in [3]. For improvement of digital literacy among students, Government of India framed a National Policy on Information and Communication Technology in School Education in [4].The initiative of ICT Policy in School Education is inspired by the tremendous potential of ICT for enhancing outreach and improving quality of education.
Teacher education needs to orient and sensitize the teacher to distinguish between critically useful, developmentally appropriate and the detrimental use of ICT. For seeing the importance of digital technology in today’s world many commissions and committees in India emphasized on the proper infrastructure in teacher education institutions and their appropriate use in teaching learning process as well as for administration purposes. National Curriculum Framework for Teacher Education (NCFTE) [5] reported that ICT can be imaginatively drawn upon for professional development and academic support of the preservice and in-service teachers. Justice Verma Commission [6] recommended that ICT may be utilized and materials developed in a decentralized and contextualized mode with participation of teachers and teacher educators for more sustained benefits. ICT should not be perceived as an ‘efficiency mechanism’ for large scale outreach only, as that assumes a ‘broadcast’ model in which the creation/control is central and the peripheries are seen as ‘consumers/users’. The real power of using ICTs is to decentralize the curricular and pedagogical processes that are currently existent.
The National Council for Teacher Education (NCTE) [7] regulation laid down guidelines about availability of ICT infrastructure in teacher training institutions. In accordance with regulation, several specialized courses are being offered in B.Ed. programme to enhance professional capacities of a student- teacher such as courses on language and communication, drama and art, self-development and ICT. A course on critical understanding of ICT is being offered as an important curricular resource. It also gives emphasis on ICT Resource Centre in the teacher educating institute and also there should be ICT facilities with hardware and software including computers, internet, TV, Camera, ICT equipment like ROT (Receive Only Terminal), SIT (Satellite Interlinking Terminal) etc. ICT must be integrated in different theories & practicum papers to develop skills and competency of prospective teachers. As per the recommendations of the NCTE regulation [7], all states have revised their curriculum, incorporated ICT in the teaching learning process and provided ICT facilities in the teacher training institute with the intention to develop digital skills of trainees.
In teacher education, digital literacy involves the development of knowledge and skills for using general computer applications, learning specific software programs and internet tools confidently and competently. It comprises several aspects, including technological awareness, technical vocabulary, components of computer, concepts of data and programs, ways of computing, working on files, documents and pictures, working with multimedia, evaluating resources and communicating with others.
Rationale of the Study
Digitalization has influenced all the aspects of human life including teaching learning. It has great potential for quality improvement of education in schools. Hence, teachers of present era should not only have content knowledge, but also, they should have pedagogical as well as technological knowledge so that they can transact knowledge to students in an advanced way. Teacher can use the digital technology for preparation, delivery and follow up of the lesson in school. Teacher can also use technology for assessment purpose as like digital portfolio. Hence, the prospective teacher must possess digital literacy for effectively dealing with digital native students in future. In this context, the Government of India and states has provided ICT facilities to all teacher training institutions. The curriculum of all teacher education courses has been revised and ICT components are included as per the NCTE regulation [7]. Hence, it is high time to examine the level of digital literacy of teacher trainees so that suitable intervention can be planed.
Recently many researchers have taken interest on the uses of digital devices and applications in teacher education. Sethy & Mohalik [8] found that all the schools have computer and projector in smart classroom, but all teachers are not using smart classroom every day for teaching learning. Barik & Mohalik [9] reported that 95% of teachers are aware about internet and effectively using for teaching and professional development and agreed that digital technology is helpful for effective teaching. Devim [10] found that B.Ed trainees’ had moderate level of ICT literacy and the urban B.Ed trainees mean scores was higher than the rural. Armistead [11] found that digital technology has significant potential to enhance learning opportunity which a student needs to be successful. Li lan [12] found that use of digital technology is significantly correlated with self-efficacy, perceived computer skill and technology access and support for both teachers and students. Oloyede [13] stated that there was no significant difference in the level of ICT literacy between male and female student teachers. Sivasankar [14] reveals that the higher secondary school teachers from English medium, teachers from urban areas and matriculation higher secondary school teachers are better in their ICT awareness than their counter parts. Tabasum, et al. [15] found that majority of the students are average in computer literacy level. Wang [16] found that digital natives misleading and disconnect student’s inside and outside classroom technology experience. Hatlevik, et al. [17] found that digital competency among secondary students is due to different factors like classroom teaching methods, home environment, language integration and academic aspirations etc. Beena & Mathur [18] reported that male M.Ed. students possess significantly higher awareness of ICT in education than female M.Ed. students and the teacher trainees of both the Government and self-financed M.Ed. Colleges have similar kind of awareness of use of ICT in education. Pattee [19] found that digital technology helps a teacher for being an effective technology user, a lifelong learner in advanced ways, make effective technological pedagogical content knowledge as well as an effective mentor and facilitator.
The above discussion reveals that attempt has been made by the researcher to examine the use of digital technology and devices in schools, colleges and teacher education institutes by the teachers and students. Mostly researches were conducted in school setting. Few studies were conducted on digital literacy of teacher trainees and teacher educators. In this context, study on digital literacy of teacher trainees is relevant.
Objectives
a) To study the digital literacy of trainee teachers at secondary level.
b) To study the extent of using digital devices for learning and teaching during internship by trainee teachers
Methodology
Survey method was used for studying the level of digital literacy and use among trainee teachers. The sample for the present study was selected randomly which consists of 170 trainees of secondary teacher training institutes of Utkal University, Odisha, India. Out of 170 trainees, 50 are from Nalini Devi Womens College of Teacher Education, 50 from Regional Institute of Education, Bhubaneswar and 70 from Radhanath Institute of Advance Studies in Education. Self-developed questionnaire based on different aspects of digital literacy and its uses such as skills and competency of using digital devices, general awareness of digital devices and applications and using digital devices for teaching learning. The validity of tools was ensured by taking expert comments. The collected data was coded numerically and entered in MS Excel for analysis. All the items were analyzed in terms of frequency and percentage and accordingly interpretation was made.
Data Analysis and Interpretation
The collected data are analyzed as per the objectives of the study by using frequency and percentage and qualitative descriptions. The detailed analysis and interpretation are presented in following pages.
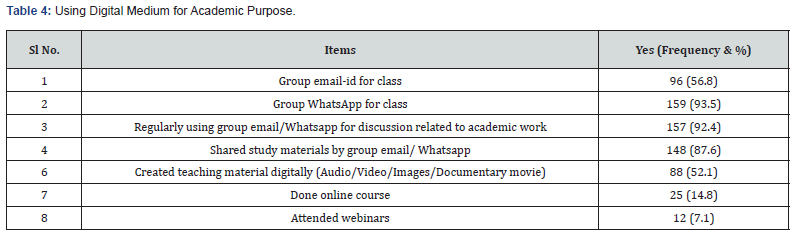
The Table 1 indicates that above 90% of trainees can change screen brightness and contrast, minimize, maximize and move window screen, use search command to locate a file and download and install applications. Further, above 50% of trainees can scan disks for viruses, write files onto USB drive, record and edit digital sound and video and only 35.8% of trainees can create and update web pages. It can be said that trainees have working knowledge of digital devices except creating and updating web pages.
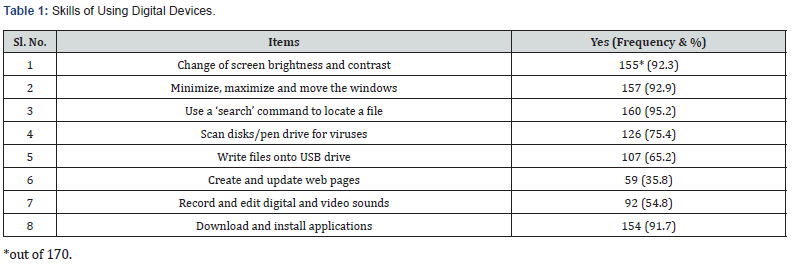
The Table 2 indicates that more than 70% of trainees have good knowledge of word processing, social networking, video sharing, web search engines and dictionary application. Further, more that 40% of trainees have good knowledge of spreadsheet, presentation and photo sharing applications. The table also reveals that more than 50% of trainees do not know learning management system, virtual worlds, podcasts and web design applications.
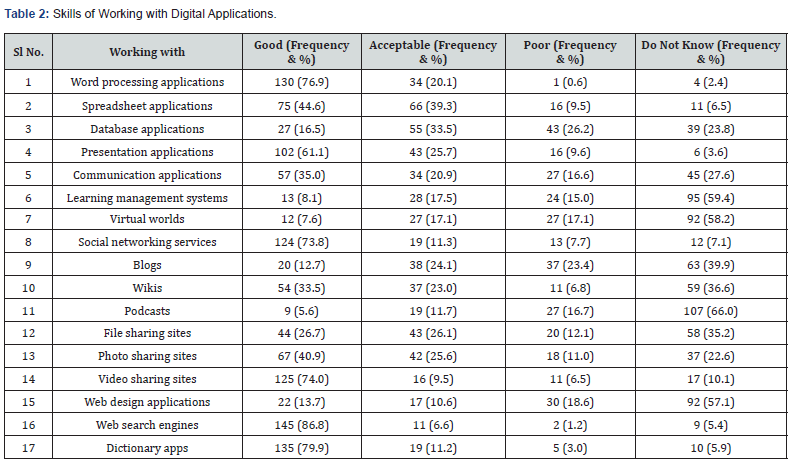
The Table 3 indicates that more than 90% of trainees are aware about the device needed to install on computer for video conference and use of Bluetooth. Further, more than 70% of trainees are aware about storage of video in camera, manage junk mail and update username and password. The table also points out that less than 50% of trainees knew about voice typing and cyber security.
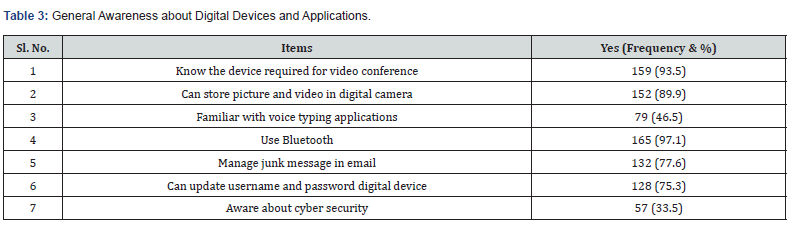
The Table 4 indicates that more that 90% of trainees use group email and whatsapp for academic work. Further, around 50% of trainees have created audio/video teaching learning materials. The table also reveals that few trainees have done online course and attended webinars.
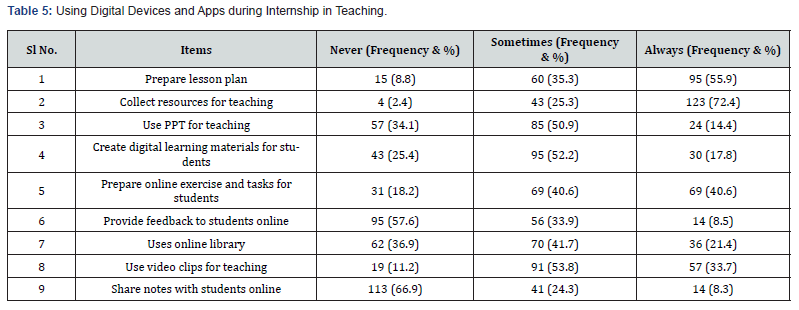
The Table 5 reveals more than 50% of trainees always use digital devices for collecting resources and preparing lesson plan during internship in teaching. Further, more than 20% of trainees use digital devices for using PPT in class, create digital learning materials, provide feedback to students, and use online library and share notes online during internship.
Major Findings
a) Majority of trainees can change screen brightness and contrast, minimize, maximize and move window screen, use search command to locate a file and download and install applications. Further, around 50% of trainees cannot scan disks for viruses, write files onto USB drive, record and edit digital sound and video and only 35.8% of trainees can create and update web pages.
b) More than 70% of trainees have good knowledge of word processing, social networking, video sharing, web search engines and dictionary application. More than 50% of trainees do not know learning management system, virtual worlds, podcasts and web design applications.
c) More than 70% of trainees are aware about storage of video in camera, manage junk mail and update username and password and less than 50% of trainees knew about voice typing and cyber security.
d) Majority of trainees use group email and WhatsApp for academic work. Around 50% of trainees have created audio/video teaching learning materials. Few trainees have done online course and attended webinars.
e) More than 50% of trainees always use digital devices for collecting resources and preparing lesson plan during internship in teaching. Only 20% of trainees use digital devices for using PPT in class, create digital learning materials, provide feedback to students, and use online library and share notes online during internship.
Educational Implications
a) Teacher educators must play great role in motivating and engaging trainees in digital devices for teaching and learning. Hence, training of all teacher educators must be organized so that they can use digital devices in teaching and assessing. They must demonstrate the uses of different digital devices in the field of school education and teacher education.
b) Present day education focuses on collaboration in learning. The digital medium can be utilized for collaboration among students and teacher educators. Hence different social networking apps like Whatsapp, Twitter, Blog, Facebook etc can be utilized for sharing and commenting in educational problems and issues so that trainee will develop skills and competencies in using ICT for learning and teaching
c) Most important skills for effective use of digital devices and services are safe practices. All the trainees must be oriented and educated in safe practices in using online services like onlinebanking, email, face book etc. They should be oriented especially in creating and changing passwords.
d) Internship is one of the significant elements of teacher training programme which provides the scope for utilizing digital devices and apps. Trainees must be motivated to use digital devices and apps for effective teaching and learning. The teacher education institute must make it compulsory for trainees to deliver specific number of lessons by using ICT. Trainees can use ICT for preparing lesson plan, preparing new teaching resources, video and audio clips which can be utilized during teaching.
e) ICT can be utilized for providing open educational resources to trainees and teacher educators. The trainees must be familiar with MOOC, NROER, e-pathasala and other online resources / libraries created by national and international agencies. Trainees must utilize these open educational resources for learning and teaching.
f) ICT must be integrated in pre-service teacher education programmes. It must not be taught as separate paper but must be given emphasis in all the papers. Because trainees must realize and understand the scope of using ICT in each paper. The potential of ICT must be utilized in learning of each perspective, pedagogy and field engagement courses.
g) All teacher education institutes must be equipped with appropriate digital devices and applications. Trainees must be given opportunities in working with computers; smart classes etc. in order to be develop their practical skills. Trainees must be oriented in the process of using smart class, smart boards and educational applications.
h) The future students will be digital native. They have different ways of learning and thinking. They want to use digital devices for everything in life from learning to education. For them, learning is fun making with subjects. Hence, prospective teachers must be equipped with all skills and competencies of using digital devices and applications.
Conclusion
The use of digital devises and application in the field of school and teacher education has been greatly emphasized by different committees and commissions at national and international level. The NCTE regulation 2014 has recommended that ICT must be integrated in all teacher education programmes, which can enable teacher trainees for using it in classroom teaching. On the other hand, the Government of India has launched the programmes such as Digital India, e-pathshala, NROER, SWAYAM etc. for facilitating the use of ICT in education sector. This study indicates that teacher training institutes are equipped with digital devices and majority of trainees have smart phone with data plan. Trainees must be encouraged and supported for using ICT in the different phases of the course. The study also indicates that trainees are using digital devices during internship in teaching programme for planning lesson, preparing teaching learning materials and for presenting the lesson. The principals of all teacher training institutes must promote the use of digital devices in admission, administration, internship and assessment of trainees. Further, mobile and mobile based learning applications must be used in teacher education programmes both by trainees and teacher educators.
To Know More About Trends in Technical and Scientific Research Please click on:
https://juniperpublishers.com/ttsr/index.php
To Know More About Open Access Journals Please click on:
https://juniperpublishers.com/index.php
To know more about Juniper
Publishers Please click on Juniper Publishers




Comments
Post a Comment